|
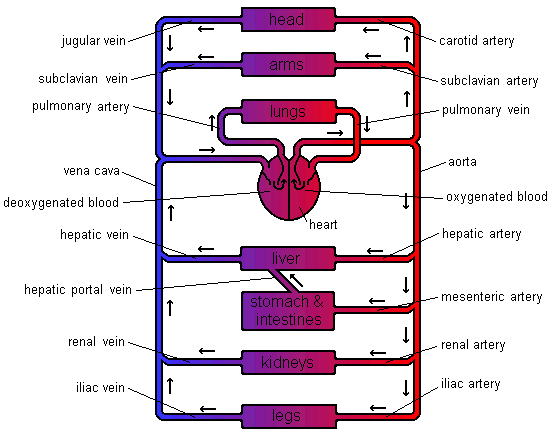
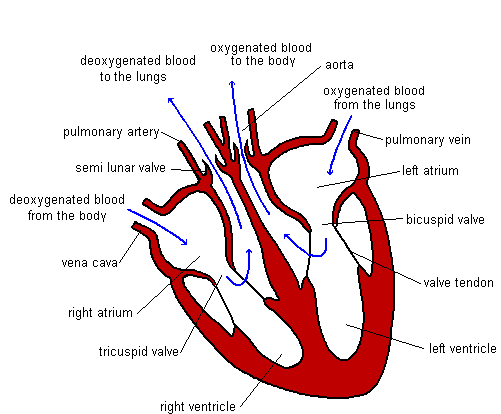
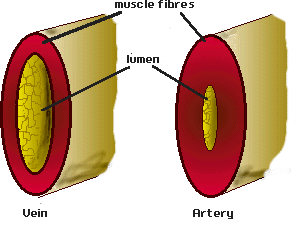
The function of the circulatory system is to transport materials around the body. There are many materials that need transporting. These include oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients (such as glucose and amino acids), hormones and waste chemicals such as urea. These substances are transported in blood through blood vessels. The blood is forced around these vessels by a pump - the heart. There are different types of blood vessels. Arteries - take blood away from the heart. Veins - take blood towards the heart. Capillaries - small vessels connecting arteries & veins. (1mm thick). Venules – smaller vessels of the veins. Arterioles – smaller vessels of the arteries. The blood travels around the circulatory system in a series of parallel circuits so that the blood travels from the heart, through an organ before returning to the heart. If the blood went through each organ in turn the organs near the end of the chain would not receive as many nutrients as the organs first in line. This is because the first organs would take out the nutrients leaving fewer for the organs that follow. There is one exception to this. The blood leaving the stomach & intestines first goes through the liver. The Liver receives its own blood supply, but this second supply gives the liver a chance to absorb any extra nutrients the body needs to store as well as neutralising any toxins that have been absorbed before they can wreak havoc throughout the body. Heart Structure The heart is really two pumps stuck together. There are two chambers to each side of the heart. The first chamber is called the atrium (atria - plural) and is the smaller of the two chambers. The larger one is called the ventricle. This chamber is the more powerful of the two as it forces blood out of the heart. The left-hand side receives deoxygenated blood from the body. The job of the left-hand side of the heart is to pump blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide. As the lungs are close by the pump does not need to be very strong. The right-hand side receives the newly oxygenated blood from the lungs and has to pump it around the rest of the body. As the distances are greater and in the case of the upper body, blood flow is against gravity, the right-hand side needs to be more powerful. Heartbeat When the heart beats it takes in blood from the veins and forces it into the arteries. The heart is really two pumps stuck together. Each pump has two chambers. When the right atrium contracts, the same happens to the left-hand side. The same is true when the right ventricle contracts. The blood must flow through the heart in one direction. Blood enters the atria from the veins and is then forced into the ventricles. The ventricles force the blood into the arteries. There are a number of sphincter muscles and valves that prevent blood flowing the wrong way. The valves are a little like parachutes. When blood flows the wrong way the valves bulge out, blocking the path. Heartbeat involves three distinct stages: 1) relaxation phase - diastole 2) atria contract - atrial systole 3) ventricles contract - ventricular systole Events in Phase Diagram (only one side shown) DIASTOLE 1) The atria and the ventricles relax. 2) The semi-lunar valves close, preventing back flow into the ventricles. 3) The elastic walls of the aorta & pulmonary artery contract, forcing blood towards the body & the lungs. 4) Blood from the veins flows into the atria, which begin to fill. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium, and oxygenated blood flows into the left atrium. ATRIAL SYSTOLE 1) The atria contract, forcing blood into the ventricles, which fill. 2) Sphincter (ring) muscles closing off the vena cava and the pulmonary veins prevents backflow from the atria into the main veins. VENTRICULAR SYSTOLE 1) The ventricles contract, forcing blood into the aorta & pulmonary artery. 2) The main heart valves (tricuspid & bicuspid) are forced shut, so preventing backflow into the atria. This happens because the pressure of blood in the ventricles is higher than the pressure in the atria. The valve cords prevent the valve being pushed back too far. 3) The walls of the aorta & pulmonary artery expand. Blood Vessels Blood vessels are tubes, which carry the blood around the body. There are different types of blood vessels. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. These vessels split up into smaller ones called arterioles. Arterioles split up into tiny blood vessels called capillaries. It is from these vessels that movement of particles to & from the blood takes place. Capillaries join together to form larger vessels called venules which join together to form veins . Heart Problems
There are a number of problems the heart can suffer from. Heart Murmur A leaky valve causes this. This means that some blood actually flows the wrong way. In minor cases this is not too much of a problem. If the leak is very bad it can cause major problems with blood flow around the body and may need corrective surgery. Pacemaker There is a special part of the heart found in the wall of the right atrium, which helps control, the speed and regularity of heartbeat. This region is called the Pacemaker as it helps control the speed of heartbeat. Sometimes problems can occur with this making the heart beat irregularly. An artificial pacemaker can be fitted to help correct this problem. An electrode is fitted to the atrium and another to the base of the ventricles. The artificial pacemaker sends out regular pulses of electricity down these electrodes to stimulate the heart to beat regularly. Heart Disease The heart is a muscle, which needs a good supply of food & oxygen in order to keep working. This is brought to the heart by the blood. If the supply of blood is halted or restricted in anyway the heart can quickly tire and then stop. This is a cardiac arrest (heart attack). A cardiac arrest can occur for a number of reasons. A high calorie diet results in excess fat in the body. Some of this fat ends up being deposited on the lining of the blood vessels. These fatty deposits can become calcified. This causes the vessels to become narrower. This problem is known as atherosclerosis. Having narrower blood vessels raises the blood pressure & the heart must work harder. If the blood vessels of the heart become blocked the blood flow to the heart will be reduced or stopped completely. Stress can increase the risk of heart failure. When under stress the heart has to beat faster. If this situation goes on then the heart is put under a great deal stress and this can lead to the heart stopping due to fatigue. Lack of exercise also increases the risk of heart disease. This is because the heart needs to be exercised like any other muscle. If it is not exercised the heart may not be able to cope when it needs to beat quickly (like running for a bus). Smoking increases the risk of heart disease because chemicals in smoke make it more likely for the blood to clot, even when still inside the body. This can cause blockages and so lead to heart failure. There is also a genetic factor. If there has been a history of heart disease in your family then this increases your chance of getting the disease.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Details
This project began as a facebook page sharing information about different illnesses, diagnosis and treatments. We are now doing short articles :)
Health stuffArchives
April 2020
Categories |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed